# Understanding Gut Health: Probiotics vs Postbiotics
Gut health is a crucial aspect of overall wellness that influences not just digestion but also immunity, mental health, and chronic disease risk. With the growing interest in gut-flourishing foods and supplements, understanding the roles and benefits of probiotics and postbiotics is essential. This blog post explores these elements in detail, helping you understand how each contributes to gut health.
## What Are Probiotics?
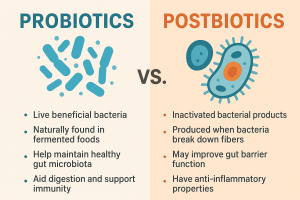
Probiotics are live microorganisms, predominantly bacteria and yeasts, that are beneficial to our health, especially the digestive system. They are often referred to as “good” or “helpful” bacteria because they help keep the gut healthy.
### Sources of Probiotics:
– Yogurt
– Kefir
– Sauerkraut
– Tempeh
– Kimchi
– Miso
– Probiotic supplements
### Benefits of Probiotics:
– **Enhancing Digestive Health:** Probiotics help balance the friendly bacteria in the digestive system.
– **Boosting Immune Function:** A healthy gut flora aids in the functioning of the immune system.
– **Preventing and Treating Diarrhea:** Probiotics can reduce the severity and duration of infectious diarrhea.
– **Improving Mental Health Issues:** Studies suggest a connection between gut health and mood and mental health.

## What Are Postbiotics?
Postbiotics are byproducts produced when probiotics metabolize in the gut. These substances include enzymes, peptides, cell wall fragments, and organic acids. Recognized for their health-promoting properties, postbiotics do not contain live organisms, offering a stable alternative to probiotics.
### Sources of Postbiotics:
– The same foods that deliver probiotics, due to the fermentation process
– Commercially produced postbiotic supplements
### Benefits of Postbiotics:
– **Supporting Immune Health:** Postbiotics can enhance immune function and reduce inflammation.
– **Protecting the Gut Barrier:** They help maintain the integrity of the gut lining, preventing harmful substances from entering the bloodstream.
– **Antioxidant Properties:** Postbiotics may help reduce oxidative stress in the body.
– **Safe for Use:** Since postbiotics are not live bacteria, they can be safer for people with compromised immune systems.

## Probiotics vs Postbiotics: Which is Better for Gut Health?
Both probiotics and postbiotics play significant roles in maintaining gut health, but their functions and benefits overlap and complement each other rather than compete. Here’s a comparison to help you understand their unique and combined benefits:
### Probiotics:
– Introduce beneficial live bacteria to the gut.
– Can be sensitive to stomach acid and may not always reach the gut alive.
– Most effective in broad-spectrum biodiversity.
### Postbiotics:
– Do not contain live organisms and are thus more stable.
– Can be beneficial where live bacteria might be risky (e.g., immune-compromised individuals).
– Provide direct health-promoting compounds.
## Conclusion
Both probiotics and postbiotics are essential for a healthy gut, with each playing its unique role in promoting health and wellness. Whether you opt for probiotics, postbiotics, or a combination of both, incorporating these elements into your diet can lead to a healthier digestive system and overall improved health.
For those looking to enhance their gut health, consider incorporating a mixture of probiotic and postbiotic-rich foods and supplements into your diet, and consult with a healthcare provider to find the best strategy for you.
### Further Reading and Resources:
– National Institutes of Health (NIH) on Probiotics and Health
– The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Postbiotics (ISAPP)
– Books: “The Gut Health Diet Plan” by Christine Bailey, “Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body’s Most Underrated Organ” by Giulia Enders
Remember, maintaining a balanced diet rich in fiber, practicing regular physical activity, and getting adequate sleep are also crucial for a healthy gut. Join the conversation on gut health by leaving your comments below or sharing this post on social media.